 The Acne is a skin disorder caused by inflammation of the sebaceous gland and hair follicle. The germs, present on the skin, cause an infection in this area with the consequent inflammatory response and the typical appearance of the lesions.
The Acne is a skin disorder caused by inflammation of the sebaceous gland and hair follicle. The germs, present on the skin, cause an infection in this area with the consequent inflammatory response and the typical appearance of the lesions.
Hormonal, hereditary and psychological factors also influence acne, which increase excess oil in the sebaceous gland.
In general, it affects adolescents and young adults, and tends to resolve over the years. Specifically, in young men it tends to be solved between 20-25 years; while in women, it can persist up to 30-40 years. The most unfavorable prognostic factor is the presence of residual deep scars, which can remain permanently.
What are the symptoms of acne?
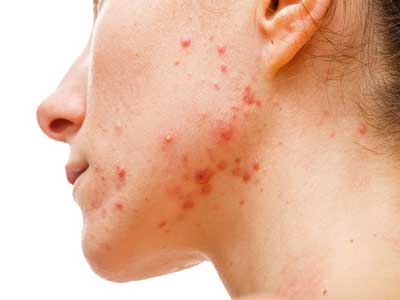
Acne manifests itself clinically with various types of lesions, and several of them may occur in the same patient.
The most common symptoms of acne are:
- Cysts on the skin
- Comedones
- Pustules
- Scars
Common acne lesions can be inflammatory or non-inflammatory.
- Non-inflammatory: closed and open comedones “blackheads”.
- Inflammatory: reddish papules, pustules, nodules and cysts.
The cystic acne, nodules and cysts forming, it requires special attention because its evolution can leave residual scars, which are the most important consequence of acne. Some patients might have additional severe types of skin problem such as fever and poor general condition (acne fulminans) and need early general treatment.
Which are the causes of acne?
The common acne vulgaris or occurs when the hair follicles of the skin become clogged by the presence of fat or dead cells. Acne is not caused directly by fat in the diet but, sometimes, the person relates it to certain foods such as chocolate, etc. In these cases, the consumption of these foods should be restricted.
Five factors mainly influence its appearance:
1. Obstruction of the pilosebaceous canal of the hair follicle due to alterations in the keratinization of the stratum corneum of the skin.
2. Increased secretion of the sebaceous glands.
3. Alterations in the bacterial microflora of the skin with the presence of microorganisms such as Propionibacterium acnes.
4. Release of inflammation mediators in the sebaceous hair follicle.
5. Hormonal variations, specifically the presence of androgens.
How does acne evolve?
The common or acne vulgaris is generally a disease that affects adolescents and young adults and tends to resolve over the years. The juvenile acne in young men, it tends to be solved between 20-25 years, while women may persist until 30-40 years. The most unfavorable prognostic factor appears in cystic acne and is the presence of residual deep scars, which can remain permanently.
The acne during pregnancy may appear sporadically by hormonal changes that occur during this stage. Normally, it is enough to take special care of the cleaning of the skin and only in the case that they do not improve, you should consult a specialist to assess the topical pharmacological
treatment.
How is acne treated?
It is important to assess the type and degree of acne to avoid aesthetic consequences Common acne treatment
Mild acne
Topical treatment is performed with exfoliants (elemental sulfur, salicylic acid, glycolic acid), benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid and retinoids (tretinoin, isotretinoin and adapalene).
Moderate acne
Topical treatment with benzoyl peroxide, retinoids, and antibiotics (clindamycin, tetracycline, and erythromycin base) is performed.
Severe acne
In these cases, systemic treatment with systemic antibiotics (tetracyclines) is necessary for 3 to 6 months. Systemic retinoids (isotretinoin) administered for approximately 5 months allow complete cure in almost all patients. In some patients it is necessary to administer more than one treatment cycle.
Very severe acne
- Systemic treatment: Isotretinoin associated with systemic corticosteroids or administered directly to the lesions.
- Surgical treatment: Drainage of cysts or mechanical removal of comedones as complementary treatments.
There are different dermatological treatments to eliminate secondary acne scars, which normally appear when there is cystic acne. These treatments should be performed as long as there are no active acne lesions.
How to remove acne marks or scars?
Among others, we have chemical peels with glycolic acid or other somewhat more aggressive methods such as dermabrasion or CO2 laser, which allow us to improve the appearance of patients. Patients with demonstrated hormonal disturbances (elevated androgen levels) may benefit from antiandrogenic or progesterone-associated estrogen therapy.
