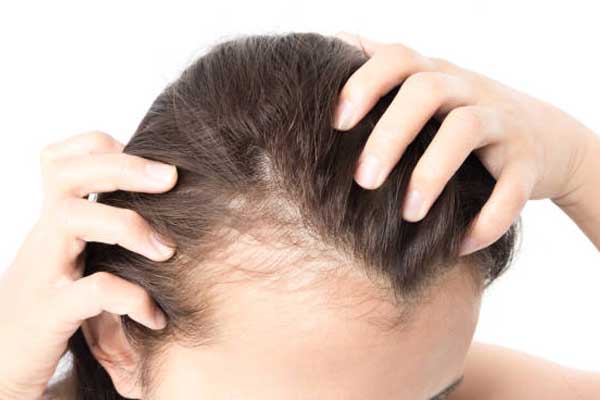
 Scalp Diseases
Scalp Diseases
The scalp is home to many diseases. Some of them are associated with hair loss, with possible impairment of the patient’s self-esteem
and quality of life. Therefore, the longer it takes to find the correct diagnosis and treatment of scalp diseases, the greater the problem and its consequences.
Dandruff
The flaking of the scalp is popularly known as dandruff. Despite being closely associated with seborrhea, dandruff can be a sign of other scalp diseases.
The main causes of dandruff are:
- seborrheic dermatitis;
- psoriasis;
- allergy or contact dermatitis;
- sun or chemical burn;
- ringworm.
As this is a non-specific sign, it is essential to assess the presence of other signs and symptoms associated with dandruff.
Redness of the scalp
A red scalp can be a normal feature of very fair people or a sign of inflammation. The dermatitis of the scalp are inflammatory conditions that may or may not be accompanied by symptoms such as pain, burning, dandruff, pimples, sores and hair loss. In some cases, redness, also called erythema, can evolve with scarring and permanent hair loss.
Some scalp diseases that can be present with redness include:
- Seborrheic dermatitis;
- Psoriasis;
- Eczema;
- Burns;
- Infections;
- Folliculitis;
- Scarring Alopecia.
Redness can be a sign of scalp diseases that lead to hair loss and permanent hair loss. Therefore, it is always recommended to assess the redness of the scalp as soon as possible.
Trichodynia: scalp pain
Although it can be extremely uncomfortable, pain is a subjective symptom. Therefore, there are several ways used by patients to describe scalp pain. Some talk about stabbing pain, stinging, pinching, tingling, prickling, burning, throbbing pain, among others. There are also those who only say that their scalp is sensitive to touch or hair manipulation. The picture of pain in the scalp is much more nonspecific than other signs and symptoms of this location.
Thus, its possibilities of causes are also broader, including scalp diseases, neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Among the main causes of scalp we have:
- Seborrheic dermatitis;
- Eczema;
- Burns;
- Hairstyle or mega hair traction;
- Infections;
- Folliculitis;
- alopecia scarring;
- Headache or headache;
- Dysthesias;
- Anxiety disorder;
- Trichotillomania;
- Fibromyalgia.
Itch
Another very frequent complaint involving the scalp is itching. When mild and sporadic, itchy scalp is not usually a major concern. But when itching starts to affect people’s daily lives or is accompanied by other symptoms such as dandruff, pain or hair loss, it can then become a problem.
Among the scalp diseases that cause itching are:
- Seborrheic dermatitis;
- Pediculosis or lice;
- Allergy;
- Ringworm;
- Bacterial infections;
- Folliculitis.
Although almost involuntary, the act of scratching the head can contribute to the worsening and perpetuation of the itching. Thus, in addition to avoiding manipulation of the scalp, it is advisable to look for a specialist doctor to detect and treat the problem.
Hair Problems
Human hair is a keratinized structure that has three stages in its normal development (hair cycle):
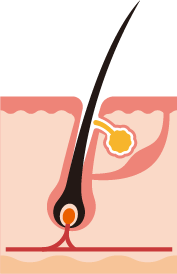
Anagen (or growth) phase
That lasts between two and six years. Hair grows and grows an inch a month on average. The follicle has a permanent activity. 90% of hair is at this stage.
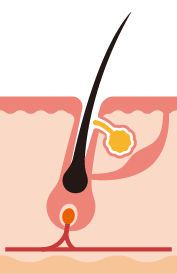
Catagen (or resting) phase
It is a stability phase that usually takes about three weeks. The hair stops growing and separates from the papilla.
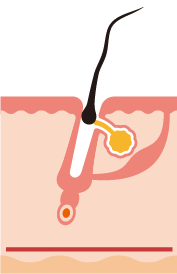
Telogen (or fall) phase
At this stage the follicle rests and starts to fall. It’s a period that lasts about 2-5 months.
Hair Follicle
It basically contains the hair, which is a keratinized structure that rests from an epidermal invagination to its depth (dermal papilla), which is where it receives cellular nutrition. The content excreted by the glands ends up in the infundibulum:
Sweat Glands
They control temperature, excreting water and other substances (salt, ammonia, uric acid, urea, lactic acid). In addition, they have an odorous function, by secreting a substance that quickly contaminates and generates our characteristic odor.
Sebaceous Glands
They produce lipids that help maintain the outer protective layer.
Each hair grows from a hair follicle and each hair follicle continues its own cycle, which is independent of those around it. Therefore, at any given time, each hair is at a different stage of its life cycle . On the scalp of a person without alopecia there are between 100,000 and 150,000 hairs, of which 85%-90% are in the anagen phase or growth period, 1-2% in the catagen or resting phase and 13-14% in the telogen phase or of fall.
85-90% OF THE HAIR IS IN ANAGENIC PHASE (GROWTH)
13-14% OF THE HAIR IS IN THE TELOGENE PHASE (FALL)
1-2% OF THE HAIR IS IN THE CATAGEN PHASE (REST)
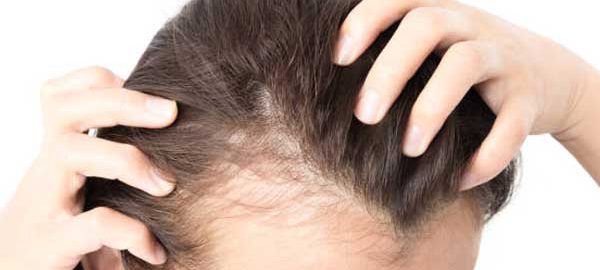
Hair Loss
We know that out of every 100 hair we have, there is always 12-15% changing, and it can take about four years to completely renew our hair.
On average, about 70-100 hairs are lost in a day, which under normal conditions are replaced by new ones that create the hair follicle.
We can say that 8 out of 10 people who believe they have alopecia does not have any pathological substrate. What happens is that the restoration of lost hair occurs randomly and not immediately. Therefore, the concept is based more on the renewal of hair follicles than on loss. This process, called telogen effluvium, often shows a seasonal trend and depends on different factors (environment or food).
However, we must also take into account the fact that there are genetic factors that cause this renewal process to have a different speed from the natural fall process that we are all subject to.
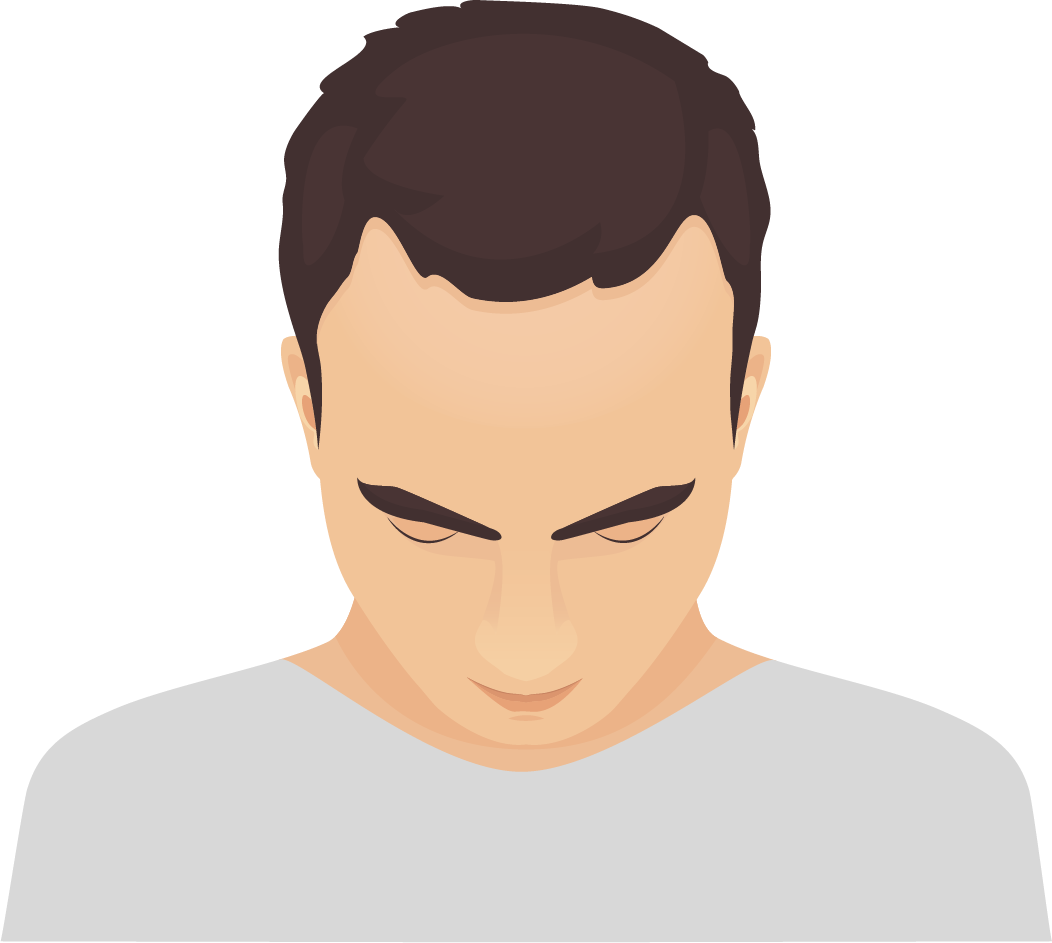

Alopecia difusa | Non-citric acid alopecia
Reversible and non-localized loss of a certain part of the scalp.
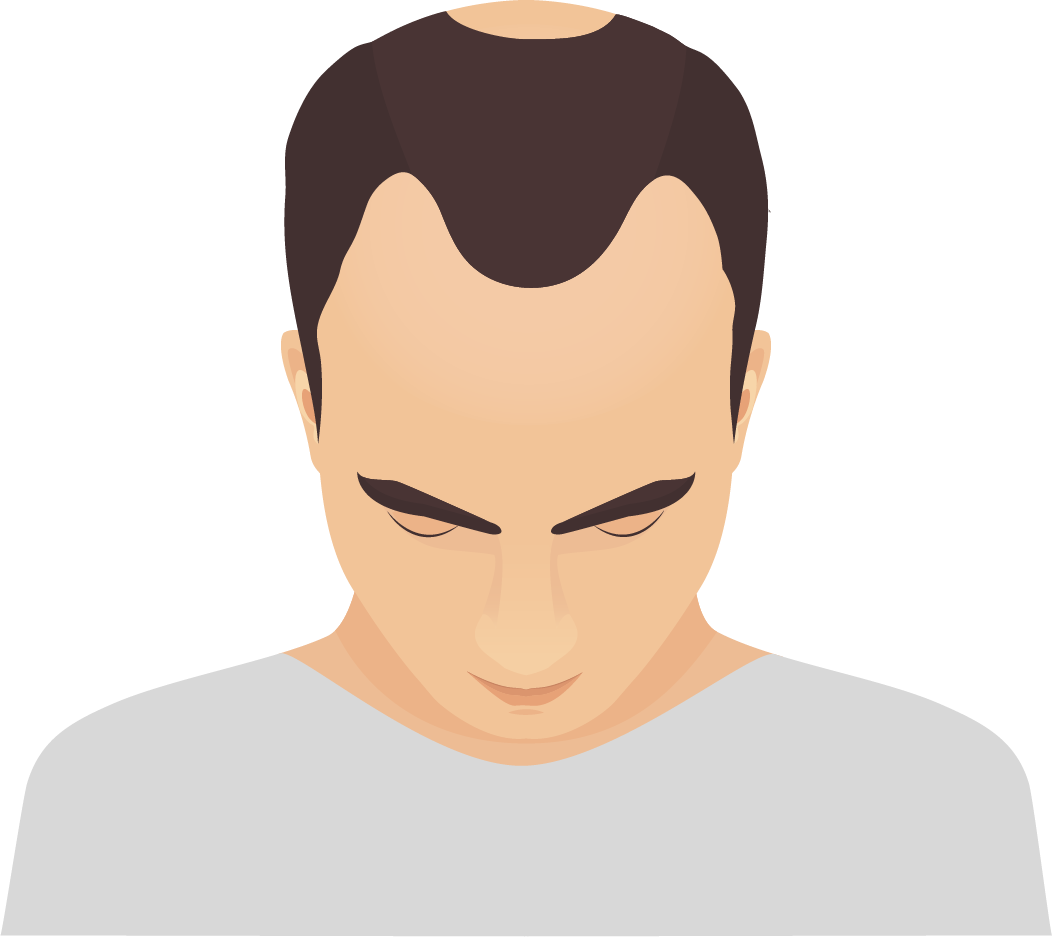

Alopecia areata | Non-citric acid alopecia
It causes circular marks and is usually reversible.
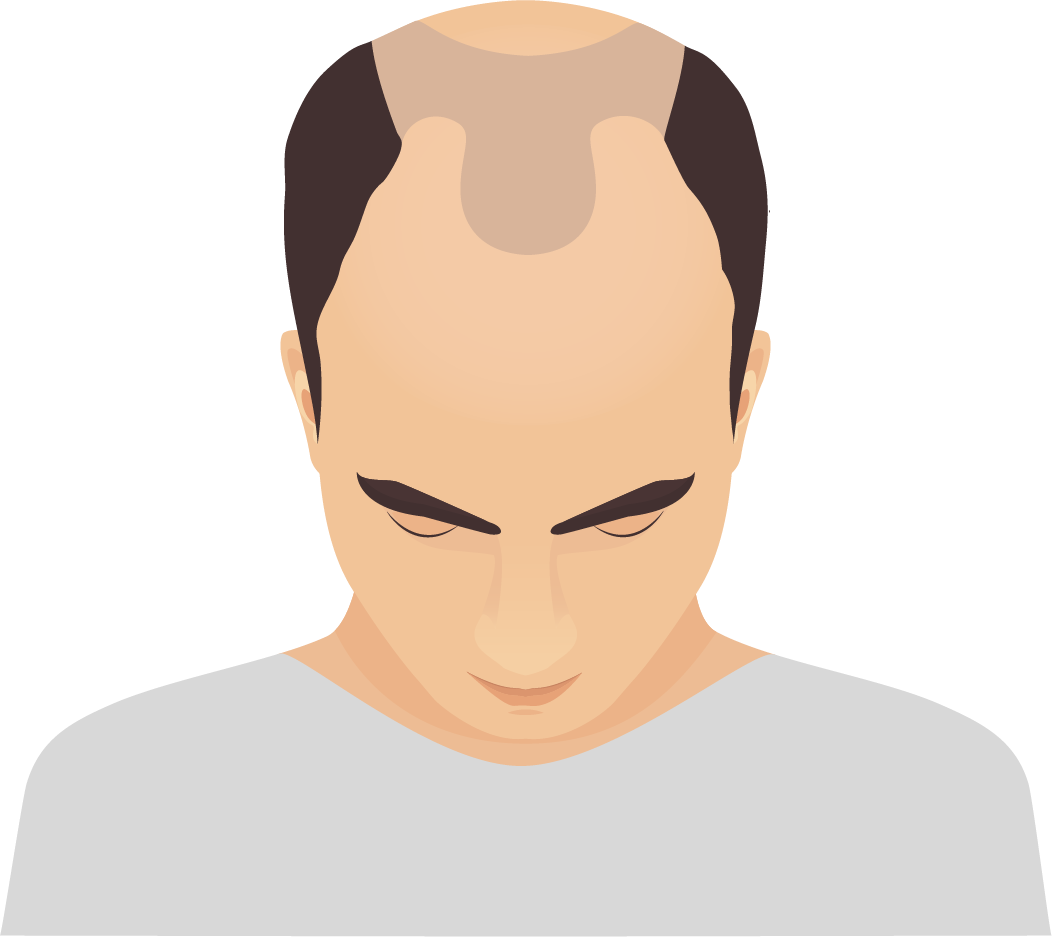

Traumatic or drug-related alopecia | non-scarring alopecia
Produced by traction or pressure trauma. Also because of trichotillomania, which is the nervous habit of pulling out your hair.
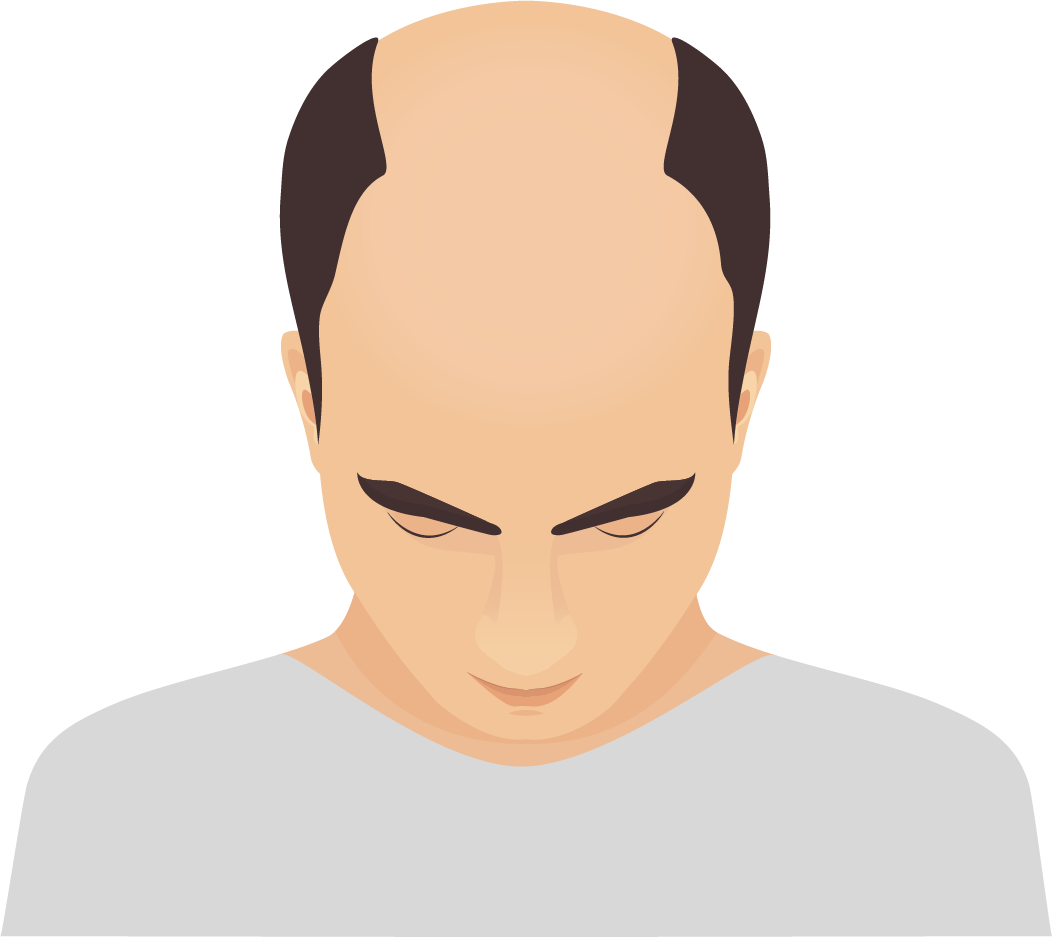

Androgenetic alopecia | Cycatric alopecia
In this type of alopecia, the hair follicle is destroyed. Hair loss is irreversible:
- Hereditary diseases : Ichthyosis, Darier’s disease, etc.
- Infectious diseases : Mycotic, bacterial.
- Neoplastic diseases : Lymphomas, metastases, etc.
- Dermatosis : Lichen, systemic lupus erythematosus, sarcoidosis, etc.
Contact
The Radiance Skin Clinic, in addition to having an appropriate structure for the evaluation and treatment of hair loss and baldness, also has a doctor who specializes in hair and professionals prepared to help with your problem. Make an assessment and get the information and care for your case.
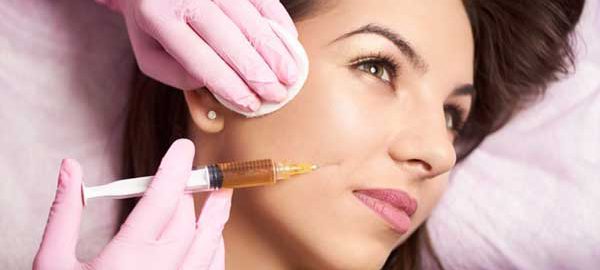
 One of the most performed aesthetic procedures in the world, facial filling with hyaluronic acid aims to attenuate static wrinkles, which are those that appear even with the face relaxed. In addition, the application of hyaluronic acid promotes skin hydration, corrects asymmetries and imperfections and is the ideal treatment to alleviate facial curves and dark circles, highlight cheekbones and fill in furrows.
One of the most performed aesthetic procedures in the world, facial filling with hyaluronic acid aims to attenuate static wrinkles, which are those that appear even with the face relaxed. In addition, the application of hyaluronic acid promotes skin hydration, corrects asymmetries and imperfections and is the ideal treatment to alleviate facial curves and dark circles, highlight cheekbones and fill in furrows.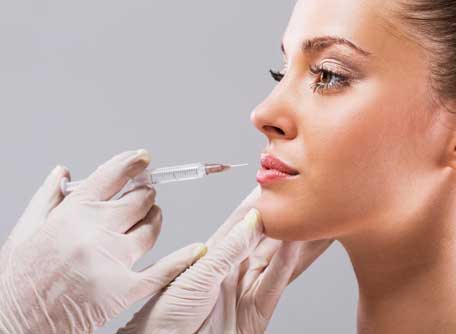
 What is Botox?
What is Botox?
 What are sexually transmitted diseases?
What are sexually transmitted diseases?
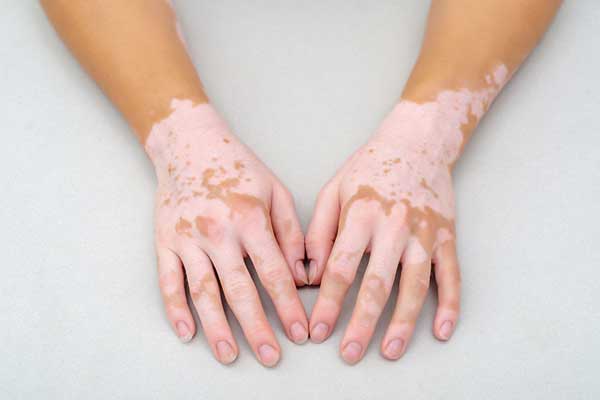


 Vitiligo and Leucoderma are two common skin conditions characterized by an external white spot on the skin. It is often difficult to tell the difference between Vitiligo and Leucoderma.
Vitiligo and Leucoderma are two common skin conditions characterized by an external white spot on the skin. It is often difficult to tell the difference between Vitiligo and Leucoderma. 
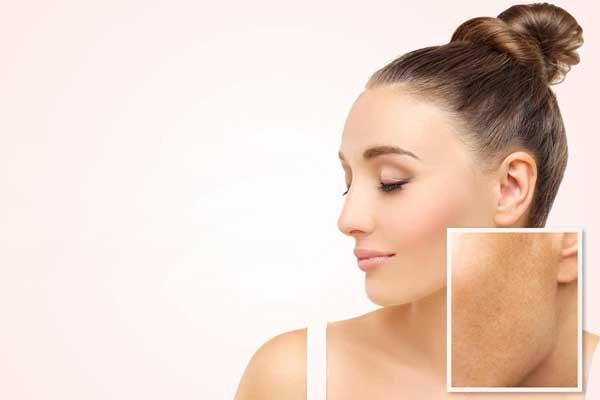
 Hyperpigmentation – What are the causes of dark spots and how to reduce them?
Hyperpigmentation – What are the causes of dark spots and how to reduce them?
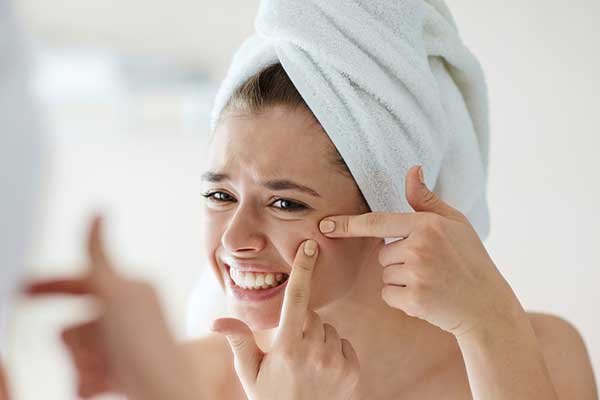
 The Acne is a skin disorder caused by inflammation of the sebaceous gland and hair follicle. The germs, present on the skin, cause an infection in this area with the consequent inflammatory response and the typical appearance of the lesions.
The Acne is a skin disorder caused by inflammation of the sebaceous gland and hair follicle. The germs, present on the skin, cause an infection in this area with the consequent inflammatory response and the typical appearance of the lesions.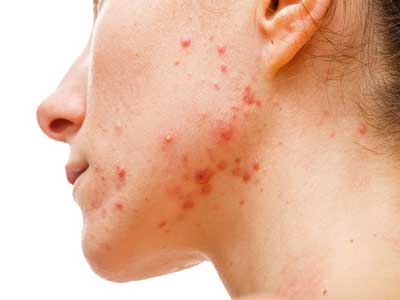
 The skin is the largest organ of the human body, dermatology is the specialty in medicine that is responsible for the study of the skin, hair and nails and their diseases. The dermatologist is the one who, after obtaining the title of general medicine, specializes in the study of the skin and its annexes (hair and nails), for the treatment of diseases or for aesthetic purposes.
The skin is the largest organ of the human body, dermatology is the specialty in medicine that is responsible for the study of the skin, hair and nails and their diseases. The dermatologist is the one who, after obtaining the title of general medicine, specializes in the study of the skin and its annexes (hair and nails), for the treatment of diseases or for aesthetic purposes.